- Treatments
- Hypertension
- Attack
- Syncope
- Heart Diseases
- Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
- Angiography Procedure
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Blocked Arteries
- Hole in the Heart
- Angina
- Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
- Heart Pacemaker
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Left Chest Pain
- Stent Surgery
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Transplant Treatment
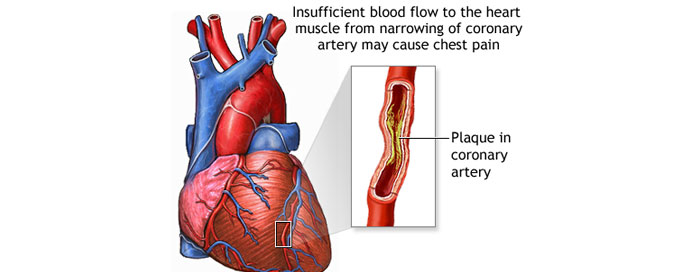
Angina
Angina is a common symptom of coronary artery disease (CAD), occurring when there is insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle. This reduced blood flow is often a result of narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, limiting the amount of oxygen and nutrients reaching the heart. Effective treatment of angina involves a multifaceted approach, addressing both immediate symptom relief and long-term management to improve overall cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Modifications
A cornerstone of angina management is adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes. Patients are often advised to follow a diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute to better cardiovascular health. Regular physical activity is encouraged, as it helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and improves overall heart function.
Medications
Several medications are commonly prescribed to manage angina symptoms and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events:
- Nitroglycerin: Nitroglycerin is a vasodilator that relaxes blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart and providing rapid relief during angina attacks.
- Beta-Blockers: These medications reduce the heart's workload by slowing the heart rate and lowering blood pressure, ultimately decreasing the heart's oxygen demand.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: These medications help dilate blood vessels, reducing the heart's workload and improving blood flow to the heart.
- Antiplatelet Medications: Drugs like aspirin or clopidogrel may be prescribed to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Revascularization Procedures
For cases where medication alone is insufficient, revascularization procedures may be considered:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: This minimally invasive procedure involves threading a catheter with a balloon into the narrowed artery. Inflating the balloon opens the vessel, and a stent is often placed to keep it open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): In cases of severe coronary artery disease, bypass surgery may be recommended. This involves using blood vessels from elsewhere in the body to create detours around blocked arteries, restoring proper blood flow to the heart.
Cardiac Rehabilitation
Participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program is beneficial for those with angina. These programs typically include supervised exercise sessions, education on heart-healthy living, and support for lifestyle changes. Exercise training can improve cardiovascular fitness, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being.
Management of Contributing Factors
Addressing underlying health conditions is crucial for comprehensive angina management. This includes managing hypertension, controlling diabetes, and optimizing cholesterol levels. Lifestyle factors such as smoking cessation are emphasized, as smoking contributes to the progression of atherosclerosis.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate angina symptoms, and learning stress management techniques can be beneficial. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness may help individuals cope with emotional and psychological factors contributing to angina.
