- Treatments
- Hypertension
- Attack
- Syncope
- Heart Diseases
- Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
- Angiography Procedure
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Blocked Arteries
- Hole in the Heart
- Angina
- Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
- Heart Pacemaker
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Left Chest Pain
- Stent Surgery
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Transplant Treatment
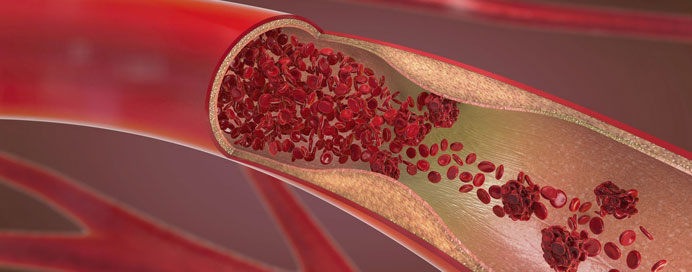
Blocked Arteries
Blocked arteries, typically involves addressing the underlying cause, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. The most common cause of blocked arteries is atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque (composed of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances) on the inner walls of arteries. Here are some common treatment approaches:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help manage and prevent the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and manage weight.
Medications
- Cholesterol-lowering medications: Statins and other cholesterol-lowering drugs can help reduce levels of LDL ("bad") cholesterol and slow down the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Antiplatelet medications: Drugs such as aspirin or clopidogrel may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Blood pressure medications: Controlling hypertension is crucial in preventing further damage to blood vessels.
Interventional Procedures
- Angioplasty and Stenting: In this minimally invasive procedure, a catheter is used to inflate a balloon in the blocked artery, widening it. A stent (a small mesh tube) may be placed to help keep the artery open.
- Atherectomy: Atherectomy involves removing the plaque from the artery using specialized catheters.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: This involves the administration of medications to dissolve blood clots.
Surgery
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): In cases where multiple arteries are blocked, or if other interventions are not suitable, CABG may be recommended. This involves bypassing blocked arteries using blood vessels from elsewhere in the body.
Medication to Manage Symptoms
- Medications such as nitroglycerin may be prescribed to relieve chest pain (angina) associated with blocked arteries.
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of the blockage, the presence of symptoms, the location of the blockage, and the overall health of the individual. Treatment plans are often individualized based on a thorough assessment by healthcare professionals.
