- Treatments
- Hypertension
- Attack
- Syncope
- Heart Diseases
- Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
- Angiography Procedure
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Blocked Arteries
- Hole in the Heart
- Angina
- Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
- Heart Pacemaker
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Left Chest Pain
- Stent Surgery
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Transplant Treatment
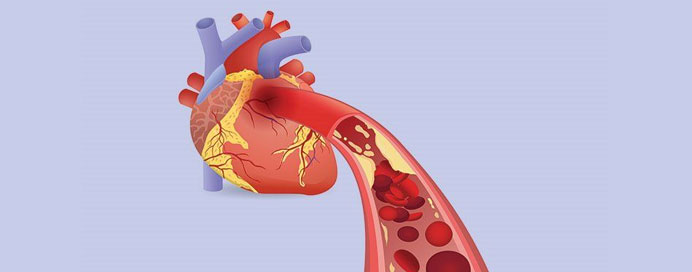
Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
The treatment of hip disorders involves a combination of conservative approaches, medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical interventions. The specific treatment plan depends on the underlying cause of the hip disorder, the severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. Here is an overview of common approaches to the treatment of hip disorders:
Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Heart-Healthy Foods: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts, which can have cardiovascular benefits.
Regular Physical Activity
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and improves overall cardiovascular health.
Quit Smoking
- Smoking is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis and heart disease. Quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of cardiovascular events.
Manage Blood Pressure
- Monitor and control blood pressure through lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, weight management) and, if necessary, medications as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Control Cholesterol Levels
- Keep cholesterol levels within a healthy range by adopting a low-cholesterol diet, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications if cholesterol levels are not adequately controlled through lifestyle changes alone.
Manage Diabetes
- For individuals with diabetes, it's crucial to manage blood sugar levels through diet, medication, and regular monitoring. Uncontrolled diabetes can contribute to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular conditions. Weight management involves a combination of healthy eating and regular physical activity.
Limit Alcohol Intake
- If alcohol is consumed, it should be done in moderation. For most adults, moderate drinking is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
Manage Stress
- Chronic stress can contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Adopt stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or other relaxation methods.
Manage Stress
- Chronic stress can contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Adopt stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or other relaxation methods.
Regular Health Check-ups
- Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health. Early detection and management of risk factors are crucial for prevention.
