- Treatments
- Hypertension
- Attack
- Syncope
- Heart Diseases
- Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
- Angiography Procedure
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Blocked Arteries
- Hole in the Heart
- Angina
- Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
- Heart Pacemaker
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Left Chest Pain
- Stent Surgery
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Transplant Treatment
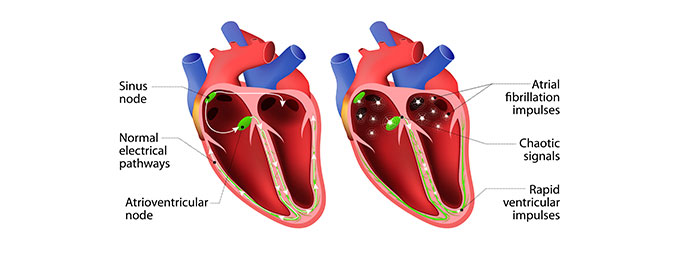
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmias, characterized by irregular heart rhythms, can range from relatively harmless to potentially life-threatening conditions. The treatment of cardiac arrhythmias involves a multifaceted approach that aims to restore normal heart rhythm, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. The choice of treatment depends on the type of arrhythmia, its severity, and the underlying cause. Here's an overview of various strategies employed in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can positively impact overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
- Caffeine and Alcohol Limitation: Some arrhythmias may be triggered by excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, and moderating intake can help manage symptoms.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial, as tobacco use is associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias and cardiovascular disease.
Medications
- Antiarrhythmic Medications: These drugs help regulate the heart's electrical impulses and are tailored to the specific type of arrhythmia. Examples include amiodarone, flecainide, and propafenone.
- Beta-Blockers: These medications reduce the heart rate and the force of contraction, making them effective in controlling atrial fibrillation and certain ventricular arrhythmias.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Drugs in this class affect calcium movement in heart cells, helping control heart rate and rhythm.
Cardioversion
- Electrical Cardioversion: This procedure involves delivering a controlled electrical shock to the heart to reset its rhythm. It is commonly used for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
Catheter Ablation
- Radiofrequency Ablation: In this minimally invasive procedure, a catheter is guided to the heart, and radiofrequency energy is used to target and destroy abnormal tissue responsible for the arrhythmia. It is often employed for supraventricular tachycardias.
Surgery
- Maze Procedure: In cases of persistent atrial fibrillation, the Maze procedure may be performed during open-heart surgery. It creates a pattern of scar tissue in the atria to disrupt abnormal electrical pathways.
