- Treatments
- Hypertension
- Attack
- Syncope
- Heart Diseases
- Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
- Angiography Procedure
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Blocked Arteries
- Hole in the Heart
- Angina
- Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
- Heart Pacemaker
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Left Chest Pain
- Stent Surgery
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Transplant Treatment
Heart Transplant Treatment
Heart transplant treatment is a complex and life-saving procedure designed for individuals with end-stage heart failure, a condition where the heart's ability to pump blood is severely compromised. This advanced medical intervention involves replacing a diseased or failing heart with a healthy heart obtained from a deceased donor. The process encompasses various stages, from patient evaluation and waitlisting to the actual transplant surgery and post-operative care.
Patient Evaluation
Before considering a heart transplant, a thorough assessment is conducted to determine the patient's eligibility. Factors such as the severity of heart failure, overall health, and psychosocial considerations are evaluated. The patient's mental and emotional well-being, as well as their support system, are crucial components of the evaluation to ensure they are prepared for the challenges associated with transplantation.
Waitlisting and Organ Allocation
Once deemed eligible, the patient is placed on a waiting list for a suitable donor heart. Organ allocation is a meticulous process that takes into account factors such as blood type, size compatibility, and medical urgency. The waiting period can vary, and patients may need to remain in close proximity to the transplant center during this time.
Heart Transplant Surgery
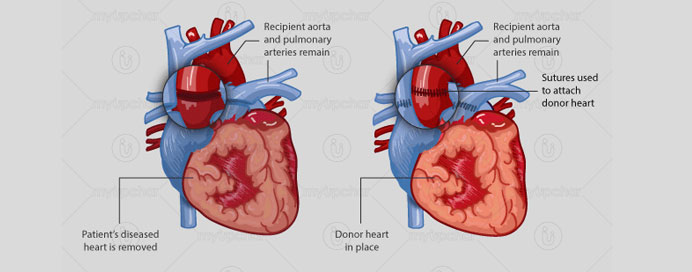
When a compatible donor heart becomes available, the transplant team proceeds with the surgery. The recipient is prepared for the procedure, and the diseased heart is removed. The donor heart is then implanted, and meticulous connections are made to ensure proper blood flow. Post-surgery, the patient is closely monitored in the intensive care unit to assess the new heart's function and address immediate concerns.
Post-Transplant Recovery and Care
The recovery phase involves a combination of immunosuppressive medications, rehabilitation, and ongoing monitoring. Immunosuppressive drugs are crucial to prevent the body from rejecting the transplanted organ. Cardiac rehabilitation aids in the patient's physical recovery and helps them regain strength. Regular follow-up appointments with the transplant team are essential to monitor the heart's function, adjust medications, and address any emerging concerns.
Complications and Considerations
Heart transplant recipients face potential complications, and vigilance is required in areas such as rejection monitoring and infection risk. Regular diagnostic tests, including biopsies, are conducted to detect signs of rejection, and adjustments to immunosuppressive medications may be made accordingly. The heightened risk of infections necessitates precautions, and recipients must promptly address any signs of illness.
