- Treatments
- Hypertension
- Attack
- Syncope
- Heart Diseases
- Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
- Angiography Procedure
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Blocked Arteries
- Hole in the Heart
- Angina
- Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At
- Heart Pacemaker
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Left Chest Pain
- Stent Surgery
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Transplant Treatment
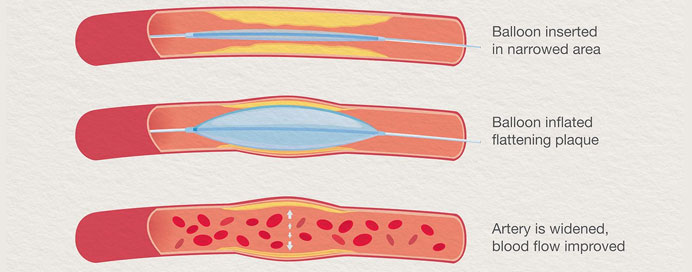
Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
Balloon angioplasty, also known as percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) when performed on coronary arteries, is a medical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels. This minimally invasive procedure is commonly employed to treat conditions such as coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and certain vascular obstructions. Here's an overview of the balloon angioplasty procedure:
Patient Preparation
- Before the procedure, the patient may undergo diagnostic tests, such as angiography, to visualize the blood vessels and identify areas of blockage or narrowing.
- The patient is usually awake during the procedure, but a sedative may be administered to help relax and reduce anxiety.
Accessing the Blood Vessel
- A local anesthetic is applied to numb the skin at the site where the catheter will be inserted. This is commonly in the groin or wrist.
- A small incision is made to access the blood vessel, and a sheath is inserted to provide a pathway for the catheter.
Guiding Catheter Insertion
- A long, thin tube called a catheter is threaded through the blood vessels under X-ray guidance.
- The catheter is carefully advanced to the site of the blockage or narrowing.
Angiography
- Contrast dye is injected through the catheter, and X-ray images (angiograms) are taken to visualize the blood vessels and identify the location and severity of the blockage.
Balloon Inflation
- A smaller balloon-tipped catheter is advanced over a guide wire to the narrowed or blocked segment.
- The balloon is positioned at the site of the blockage, and it is then inflated. The inflation compresses the plaque or fatty deposits against the vessel wall, widening the artery and restoring blood flow.
Deflation and Removal
- After a brief period of inflation, the balloon is deflated and removed.
- The improved blood flow is confirmed through angiography, ensuring that the blockage has been successfully treated.
Deflation and Removal
- After a brief period of inflation, the balloon is deflated and removed.
- The improved blood flow is confirmed through angiography, ensuring that the blockage has been successfully treated.
Balloon angioplasty is a commonly performed and effective procedure for treating narrowed or blocked blood vessels. While it often provides immediate relief and improves blood flow, patients may still need to make lifestyle changes and take medications to manage underlying conditions and reduce the risk of further vascular issues. The decision to perform balloon angioplasty is based on factors such as the location and severity of the blockage, the patient's overall health, and the presence of other cardiovascular conditions.
